|
|
Breast Reconstruction - After Breast Cancer
As might be unexpected, breast reconstruction is controversial....in the media and even amongst physicians. Early in its history, physicians were concerned that surgery to restore the breast was potentially problematic to the continued screening of the patient for recurrent cancer. Advanced breast cancer should be treated aggressively. In these women it might be best to delay or even withhold breast reconstruction. For the majority of women presenting with early disease. immediate reconstruction is low risk.
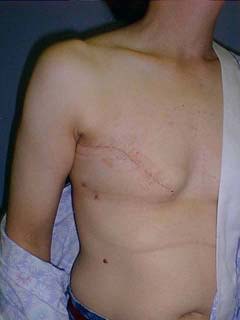
The Basics of Breast ReconstructionThe basic variations are:(1) Immediate versus Delayed Reconstruction (2) Implant-based versus Tissue-based Reconstruction Immediate Reconstruction starts at the time of mastectomy. In this case breast mound reconstruction directly follows the cancer operation. Obviously, Delayed Reconstruction occurs some time following mastectomy either because of patient preference, patient health or extensive cancer at mastectomy. Implant-based Reconstruction involves the use of breast implants and tissue expanders. Breast mound reconstruction is facilitated by stretching the skin with a balloon (Expander). A later operation is performed to remove the expander and place a permanent implant. Tissue-based Reconstruction involves the use of the patient's own tissues most often moved from the abdomen or back to provide volume for a breast mound. In some cases, one or the other type will be recommended. The tissue-based versions provide a better aesthetic result but require a larger operation and more disability to get there. At this point in the United States, about 70% of breast reconstructions are performed using Expanders and implants. A example of an implant reconstruction follows: An Immediate Breast Implant Reconstruction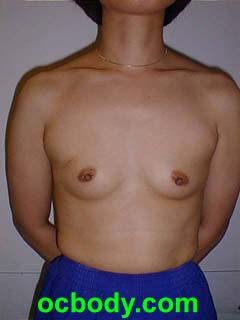 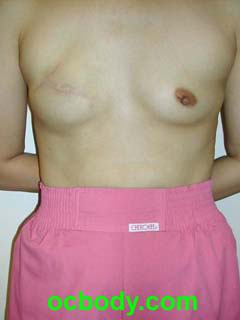 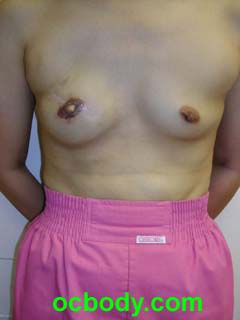
This young woman had an early invasive breast cancer. She chose mastectomy and wished an immediate reconstruction with as little as possible opposite breast surgery. She was neither a smoker nor a diabetic and it was not predicted that she would need post-operative radiation therapy. A skin-sparing mastectomy was performed by her general surgeon after which Dr D placed a small breast implant. This is sometimes possible in patients with healthy skin following mastectomy A year later, she chose to have nipple-areolar reconstruction, an outpatient operation. Tissue Expansion TechniqueTissue Expansion can offer favorable results, but is more susceptible to the variable healing after mastectomy, chemotherapy and radiation therapy than tissue-based techniques. It is easier on the patient from the disability standpoint. An example is laid out HERE.Breast Reconstruction Surgery and RiskReconstruction of the breast following Mastectomy is very different than cosmetic breast surgery. The outcome is rarely as pleasing, but the alternative as seen above is not so pleasing either. The risk of problems in reconstruction dwarfs that in cosmetic surgery as well:
Dr Di Saia for Breast ReconstructionDr Di Saia is a board-certified plastic surgeon who was first certified in general surgery. In years gone by, he used to perform the breast removal surgery. He much more enjoys the process of creating a new breast for you. He also enjoys the challenge of improving breast reconstruction cases in which other surgeons have said it cannot be done. See some of these cases from our main breast section here.
More Information on Breast Implants in Reconstruction
© John Di Saia, MD... an Orange County California Plastic SurgeonServing Southern California since 1997 * (949) 369-5932
|
| ||||||||||||||